
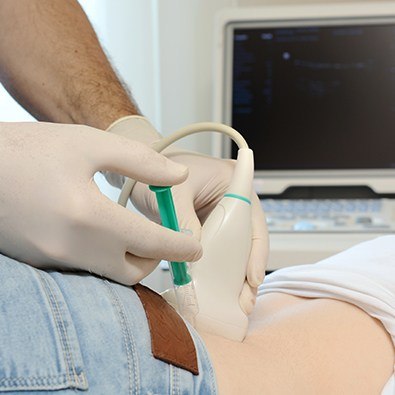
Generalized mild, dull, and achy pain to the deep or lateral or anterior shoulder, with occasional radiation to the proximal arm.
Nerve injuries should be considered as part of the differential diagnosis process when a patient reports pain, weakness, or paresthesias. It is important to note that the clinical presentation of axillary nerve dysfunction is variable and can easily go undetected, as the dislocation or fracture may mask the symptoms. 5th degree nerve injury= complete disruption of the nerve.4th degree nerve injury= axon, endoneurium, and perineurium are damaged with preservation of the epineurium.3rd degree nerve injury= axon and endoneurium are damaged with preservation of the perineurium.Connective sheath damage ranges from partial disruption of the endoneurium to complete disruption of the involved nerve.Comparable to a 2nd degree degree nerve injury.The endoneurium acts as a guide for axonal regeneration.Axonal damage is present with preservation of the endoneurium.Comparable to a 1st-degree nerve injury (Sunderland's Classification of Nerve Injury).The axon and all 3 connective tissue layers (endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium) remain intact with a decrease in conduction.

Help manage expectations as a clinician with this type of injury. Therefore the recovery can be long and discouraging for the patient at times. Nerve Injury Overview Īs a reminder, nerve regeneration takes place at a rate of an estimated ~1 millimetre (mm) per day.

įigure 2- Axillary nerve within the quadrilateral space. The axillary nerve is susceptible to injury at several sites, including the origin of the nerve from the posterior cord, the anterior inferior aspect of the subscapularis muscle and shoulder capsule, the quadrilateral space, and within the subfascial surface of the deltoid muscle.
#Nerve safety last free#
Propagated tension due to overstretching of the axillary nerve over the humeral head during shoulder dislocations may cause elongation of the free portion of the axillary nerve and the increased tension may even result in axillary nerve avulsions from the posterior cord of brachial plexus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
